Main Takeaway:
The India Energy Stack (IES) is a pioneering Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) launched by the Ministry of Power to transform India’s power sector. By creating a secure, interoperable platform modeled on India Stack and UPI, IES aims to enhance DISCOM efficiency, enable smart‐grid operations, empower consumers, integrate renewable energy, support smart homes, and advance India’s Net Zero commitments.
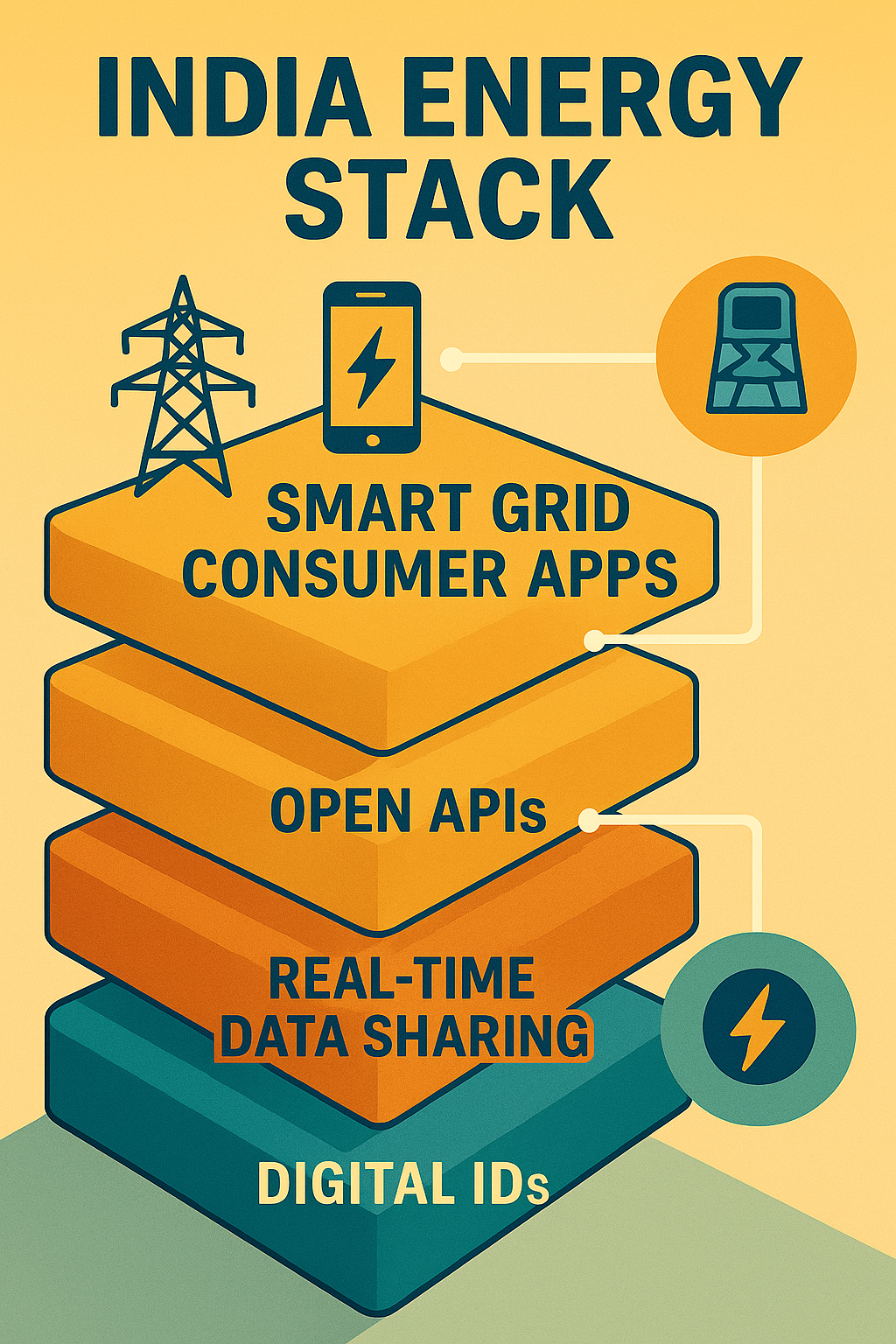
India Energy Stack layered architecture
Background and Rationale
India’s power sector is undergoing rapid change driven by:
- Surging renewable capacity and variable generation patterns
- Rising electric vehicle (EV) adoption and bidirectional demand
- Growing consumer participation through distributed generation and prosumers
However, fragmented legacy systems, siloed data, and lack of real-time integration hinder grid stability, efficiency, and innovation. The IES addresses these challenges by establishing a unified digital backbone for the entire electricity value chain.
Key Features of the India Energy Stack
- Unique Digital IDs
Each consumer, asset (e.g., transformers, solar panels), and transaction receives a standardized identifier, enabling consistent tracking and authentication across platforms. - Real‐Time, Consent-Based Data Sharing
Consumers and utilities can share data instantly under user‐controlled consent, fostering transparency and personalized services without compromising privacy. - Open APIs and Modular Architecture
Standardized interfaces allow legacy systems, third-party applications, and new technologies to plug into the IES seamlessly, driving innovation and competition. - Utility Intelligence Platform (UIP)
A proof-of-concept analytics toolset built on IES that offers real-time dashboards, predictive outage management, demand forecasting, and asset diagnostics to DISCOMs and policymakers. - Consumer Empowerment Tools
Portals and mobile apps enable consumers to monitor consumption, participate in demand-response programs, choose green tariffs, and lodge service requests swiftly.
Governance and Implementation Roadmap
- Task Force Composition: A 17-member body chaired by Nandan Nilekani (non-executive chairman, Infosys) and Ram Sewak Sharma (former DG, UIDAI), with expert representation from technology, regulatory, and power sectors to steer IES development and scale-up.
- 12-Month Proof of Concept (PoC):
– Pilot Utilities: Selected DISCOMs in Mumbai, Gujarat, and Delhi will trial UIP and API integrations to validate real-world use cases.
– Public Consultation White Paper: The Task Force will release a draft IES white paper for stakeholder feedback, ensuring inclusivity and governance clarity.
Strategic Impacts
1. Renewable Integration
Real-time grid monitoring and two-way data flows enable efficient management of variable renewables, reducing curtailment and optimizing dispatch for solar and wind projects.
2. Smart Grid Operations
Digital twins of network assets, demand-response triggers, and automated fault detection enhance grid stability and reduce Aggregate Technical & Commercial (AT&C) losses, improving DISCOM financial viability.
3. Smart Homes and Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
Seamless onboarding of rooftop solar, home batteries, and EV chargers into the IES ecosystem empowers prosumers to trade surplus energy, participate in ancillary markets, and bolster demand flexibility.
4. Consumer Participation and Market Access
Transparent real-time billing, green‐tariff options, and peer-to-peer energy trading platforms democratize energy markets, fostering competitive pricing and service innovation.
5. Advancing India’s Net Zero Goals
By standardizing data flows and enabling decarbonization solutions at scale, IES underpins India’s commitment to achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2070, facilitating policy design, monitoring, and enforcement.
UPSC Preparation Strategy
Key Topics & Concepts:
- Digital Public Infrastructure: India Stack, UPI, Aadhaar parallels
- DISCOM reforms: AT&C loss reduction, financial restructuring
- Smart grids: Demand response, real-time monitoring, microgrids
- Renewable integration: Grid codes, forecasting, energy storage
- Energy policy and governance: Task Force roles, regulatory frameworks
Sample Questions:
- Examine how the India Energy Stack can address structural inefficiencies in India’s power distribution sector.
- Assess the implications of real-time, consent-based energy data sharing for consumer empowerment and privacy.
- Discuss the role of digital public infrastructure in achieving India’s renewable energy targets and Net Zero commitments.
By establishing a robust, interoperable digital backbone, the India Energy Stack marks a transformative leap toward a smarter, greener, and consumer-centric power sector, aligning with India’s broader economic and environmental goals.
