Main Takeaway:
As India completes eight years of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on 1 July 2025, the regime stands validated by record collections, an expanded taxpayer base, and significant benefits for MSMEs, logistics, and transparency—foundational to India’s journey toward a unified, formal economy.
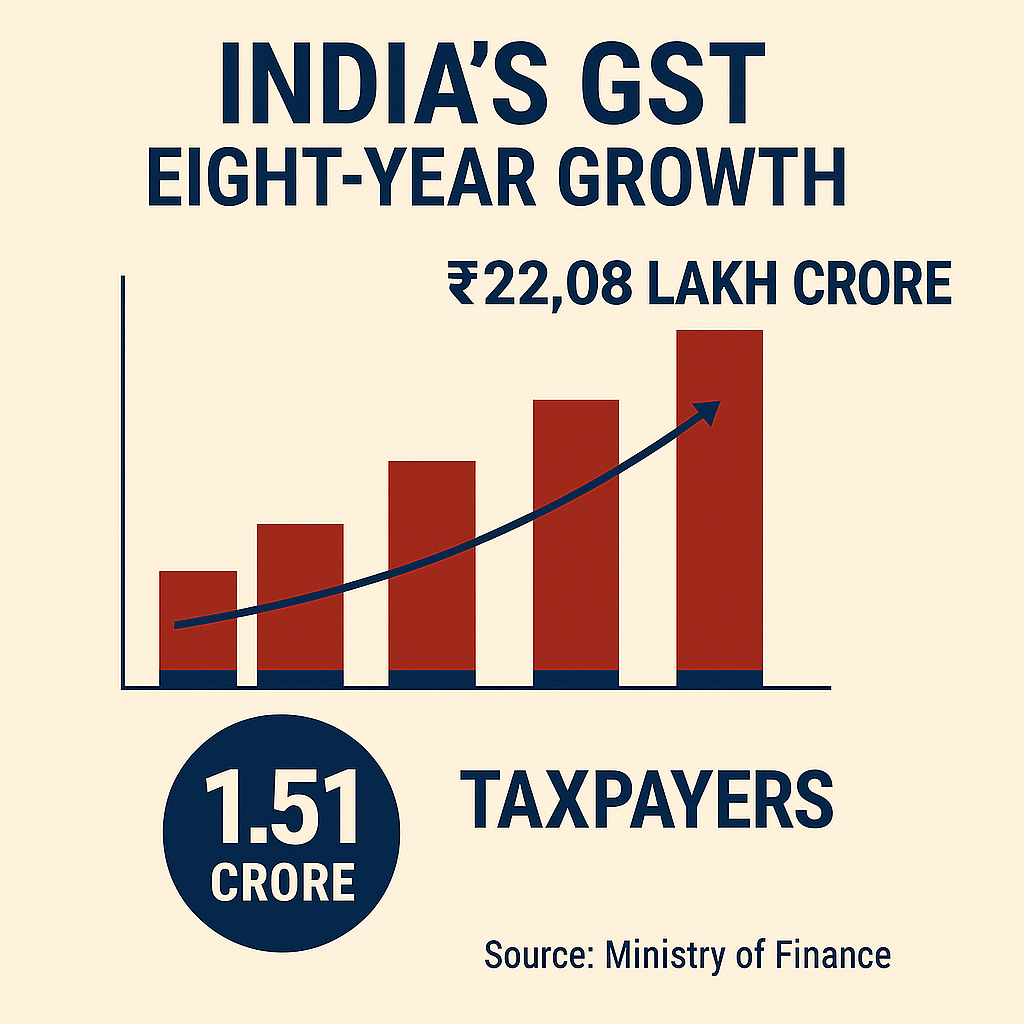
Record Collections and Growth
India’s gross GST collections for the financial year 2024–25 reached a historic ₹22.08 lakh crore, marking a 9.4% year-on-year increase over the previous year. This achievement underscores the progressive formalization of the economy and stronger tax compliance mechanisms. The average monthly collection during FY 2024–25 was ₹1.84 lakh crore, up from ₹1.68 lakh crore in FY 2023–24.
Expansion of the Tax Base
Since its launch on 1 July 2017 with around 65 lakh registrations, GST has more than doubled its registered taxpayer base to 1.51 crore active registrations as of 30 April 2025. This growth reflects broader coverage of businesses and improved compliance infrastructure.
India GST eight-year performance infographic
Benefits to MSMEs
GST has significantly eased the compliance burden for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) by:
- Raising exemption thresholds: Initial ₹20 lakh limits for goods were enhanced to ₹40 lakh, reducing compliance pressure on small traders and manufacturers.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): MSMEs can offset GST paid on inputs against their output liability, improving cash flow and competitiveness.
- Interstate Market Access: Unified tax structure removes state-border barriers, facilitating business expansion beyond local markets.
Improved Logistics and Transparency
By subsuming over 17 local taxes and 13 cesses into a five-slab structure (5%, 12%, 18%, 28%, and special rates), GST has:
- Streamlined supply chains, reducing transit times and logistics costs.
- Enhanced real-time tracking of goods movement via e-way bills, curbing tax evasions.
- Standardized digital invoicing, promoting audit trails and transparency.
Holistic Impact on Governance and Economy
- Fiscal Health: Record GST revenues bolster central and state finances, enabling increased public spending without compromising fiscal prudence.
- Ease of Doing Business: Timely reforms—such as simplifying return filing and upgrading the GST portal—have contributed to India’s improved rankings in global business indices.
- Formalization: A wider tax net brings more enterprises into the formal economy, facilitating better policy targeting and social security coverage.
Conclusion
Eight years after its inception, GST has not only achieved record revenues but also driven key structural reforms—expanding the tax base, empowering MSMEs, and enhancing transparency in indirect taxation. For UPSC and competitive-exam aspirants, understanding this transformative reform is crucial for comprehending India’s evolving economic governance.
1 PIB: Eight Years of GST – Press Note, 30 June 2025.
2 GSTClub: “India’s GST collections hit an all-time high of ₹22.08 lakh crore in FY25,” 30 June 2025.
3 Deccan Herald: “Gross GST collections double in 5 years to record Rs 22.08 lakh cr in FY25,” 30 June 2025.
